Jainism All Important Notes
Jainism
▪ Jainism is of ancient origin & believed to have 24 Tirthankaras / Great teachers in their religion
▪ 1st one was Rishabdev (Born in Ayodhya) who is said to have laid the foundation of orderly human society & realised t hat the source of Jaina philosophy was Adinath.
▪ 23rd was Parshavnath (Born in Varanasi) & Last and 24th was Vardhamana Mahavira (Born 540 BC at Kundangrama near Vaishali)
Vardhamana Mahavira
▪ In search of truth Mahavira abandoned the world at the age of 30 & became ascetic & medicated for 12 years practicing austerities.
▪ In 13th year, at the age of 42, he attained Kaivalya (Juan) under Sal tree at Timbhikagrama
▪ Kaivalya → One who conquered misery & happiness → And because of this conquest he is known as Mahavira or great hero or jina (the conqueror) & his followers Jainas
▪ He propagated religion for 30 years & passed away at the age of 72 at Pavapuri near Rajgir
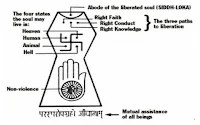
3 principles of Jainism → Triratnas
▪ Right faith (believe in teachings & wisdom of Mahavira)▪ Right Knowledge (Acceptance of theory that there is no god & world has been existing without a creator & all objects possess a soul)
▪ Right conduct (Refers to observance of 5 great vows)
- 1. Ahimsa
- 2. Satya
- 3. Asteya (Not to steal)
- 4. Parigraha (Not to acquire property)
- 5. Brahamcharya (observe continence / not to led immoral life → added by Mahavira)
Teaching of Jainism
▪ Rejected the authority of Vedas & objected to Vedic rituals & sacrifices▪ Even practice of agriculture was considered sinful as it caused injury to earth, worms & animals
▪ Doctrine of ascetism & renunciation was carried to great lengths by practice of starvation, Nudity & other form of self-tortures (Penance for all sins committed)
▪ Although Parvanath (23rd Teacher) asked people to cover their upper & lower body part but Mahavira asked them to discard cloths altogether ( Extreme austerity)
▪ Mahavira did not condemn Verna system as Buddhism did as according to Mahavira , a person born in higher or lower verna is the consequences of the sins of past life & through penance & meritorious life they can attain liberation
▪ Jainism mainly aimed at freedom of Individual from worldly bonds
Twelve small vows (anuvrats) of Jainism
Five anuvrats- 1. avoiding injury to mobile beings which have two or more senses or desisting from deliberate acts of violence
- 2. truthfulness to avoid false statements out of extreme affection for someone or out of hatred for someone
- 3. refraining from taking anything not given
- 4. desisting from sexual relationship with anyone other than one’s spouse
- 5. voluntarily limiting the possession of all forms of assets
The Seven supplementaries
- 1. refraining from movement beyond a limited area
- 2. restricting a movement to even a more limited area
- 3. refraining from wanton destruction of the environmentby thought, word or deed
- 4. keeping aloof from a sinful conduct for a set period of time (observing samayik)
- 5. fasting on sacred days and observing special restrictions at secluded places
- 6. limiting the use of consumable and non-consumable goods
- 7. Sharing your food or resources with guests or wandering ascetics.
Spread of Jainism
▪ Admitted both women and shudras in its order of followers▪ Used prakrit (common language) for preaching instead of sanskrit
▪ 200 years after the death of Mahavira, there was a serious famine in Ganga valley. Many Jain
followers led by Chandragupta Maurya & Bhadrabahu left for south (Karnataka) & rest stayed back under the leadership of Sthalbahu. Emmigrants spread Jainism in south India.
▪ Meanwhile Sthalbahu changed the code of conduct for the monks which led to division of Jainism into 2 sects Swetambars (White clad / Northerners) & Digambars ( Naked / Sky Clad / Southerners)
▪ 1st Jain council was held at Pataliputra led by Sthalbahu & 2nd was held at Valabhi where 12 Anagas
of Swetambars were finally compiled Contribution of Jainism
▪ 1st serious attempt to mitigate evil of verna system & ritualistic vedic system
▪ Adoption of Prakrit by Jainas helped in its growth & many regional languages grew out of Prakrit especially Shauraseni, out of which Marathi grew
▪ Jainas composed earliest important work in “ Apabhramsha” & prepared its 1st grammar
▪ Jainism also contributed to the growth of Kannada
▪ Basadis → Jains Monastic establishments
▪ Jainism religious literature is written in “Ardhamagadhi” & text were finally compiled at Valabhi (Gujrat)