Buddhism All Important Notes
Buddhism
▪ Founded by Gautam Buddha (Original Name → Siddhartha)▪ Born in 563 BC at Lumbini in Nepal near Kapilavastu (As a kshatriya in Shakya clan)
▪ Parents → Suddhodhana & Mahamaya
▪ Left Home at the age of 29 in search of truth & did intense penance & meditation
▪ Attained Nirvana under a Pipal tree at Bodh Gaya & henceforth known as Buddha (The enlightened one)
▪ Delivered his 1st sermon at Sarnath (Banaras) & died at the age of 80 at Kushinagar (U.P)
Noble truth by Buddha
▪ World is full of sorrow▪ People suffer on account of desires
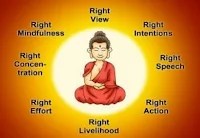
▪ If desires are conquered, Nirvana can be achieved i.e. free from cycle of birth & death & which can be done by following 8 fold path (ashtangika marga):
- Right Understanding
- Right Determination
- Right Speech
- Right Action
- Right livelihood
- Right Exercise
- Right Mindfulness
- Right Medication
Tri Ratnas of Buddhism
- ▪ Budhha (The enlightened)
- ▪ Dhamma ( Doctrine of Buddhism)
- ▪ Sangha (Order of Buddhism)
Teachings by Buddha
▪ Budhha was a practical reformer & did not believe in soul or god or metaphysical world & concerned himself with the worldly problems▪ Suggested that a person should avoid excess of both, Luxury & Austerity & prescribed a middle path
▪ Laid great emphasis on Karma (Varna based on action not on birth) & Ahimsa
▪ Opposed varna system & laid down the principle of social equality
Spread of Buddhism
▪ Buddhism had 2 kinds of disciples – Monks (Bhikshus) & Lay worshippers (Upasikas)▪ Monks were organised into sangha for the purpose of spread of Buddhist teachings
▪ Membership was open to all, Male or female without any cast distinction, but every member had to take vow of continence, poverty & faith (Penance to achieve liberation )
▪ Use of Pali language also contributed to the spread of Buddhism
Buddhist Text
Tripitakas → All written in Pali Language▪ Sutta-pitaka
▪ Vinaya-pitaka
▪ Abhidhamma-pitaka
Contribution of Buddhism
▪ Slaves & debtors couldn’t join sangha rule helped moneylenders & richer sections of society▪ Earliest Budhhist text “ Suttanipata” pleads for protection of cattles & helped to prevent their decimation
▪ Taught people to put reason in everything & pleaded for logic instead of superstitions hence promoted rationalism in people
▪ Promoted education through residential universities like Valabhi, Nalanda & Vikramshila
▪ Formed Hybrid Sanskrit by mixture of Pali & Sanskrit
Cause of Decline
▪ Revival of Brahmanism & rise of Bhagavatism▪ Use of Sanskrit instead of Pali from 4th Buddhist council (Around 100 AD)
▪ After birth of Mahayana, Practice of Idol worship, Huge offerings & donations became common & led to the deterioration of moral standards
▪ Attack of Hunas (Around 500 - 600 AD) & Attack of Turkish invaders (1200 AD) destroyed major Buddhist Monasteries
▪ Brahamana ruler Pushyamitra have said to persecuted Buddhists
▪ Shaivite Shashanka have said to cut the original Bodhi tree at Bodhgaya
Buddhist Councils
1st Council → Rajgir
▪ Was held immediately after the death of Buddha at Saptaparni cave in which the unwritten teachings of Buddha were penned down after his death.▪ Held at Rajgir under the patronage of Ajatashatru under the chairmanship of Mahakashyap
▪ Ananda composed Suttapitaka (Buddha’s Teachings) & Upali composed Vinaypitaka ( Monastic code for Buddhism)
2nd Council → Vaishali
▪ Was held approx. 100 years after the death of Buddha under the patronage of King Kalasoka under the chairmanship of Sabakami▪ Mainly due to 10 disputed points under Vinaypitaka (Monastic codes of Buddhism)
3rd Council → Patliputra
▪ Held under the patronage of Ashoka under the chairmanship of Mogliputra tissa▪ Compilation of Abhidhamma pitaka took place (Philosophical exposition of Budhhism)
▪ Budhhism preached & Propagated by Ashoka is known as Hinyana
4th Council → Kashmir
▪ Held under the patronage of Kanishka under the chairmanship of Vasumitra▪ Resulted in division of Buddhism into Hinyana & Mahayana
▪ Asvaghosa participated in this council & all the deliberations were made in Sanskrit
Origin of Mahayana Buddhism
▪ Monks around beginning of Christian era started to accept huge cash & donations & even started accepting non-vegetarian foreigners in Sangha▪ Monks became more lax in day to day life, started accepting gold & silver, started eating non-veg food & started wearing elaborated robes
▪ Disciples even deserted religious order of Sangha & resumed their householder’s life; Started using Sanskrit instead of Pali & started worshipping statues of Buddha & started practicing rituals instead of his symbols.
▪ This new kind of Buddhism was known as Mahayana (Greater vehicle) & Hinyana (Lesser vehicle); the former believed in image worship, rituals and Bodhisattvas, (incarnations of Buddha) while the latter continued the practices of the earlier Buddhism.
| Mahayana | Mahayana Hinyana |
|---|---|
| Individual as center & firm to letter of Buddhist teachings | Sangha as center & firm to essence of Buddhist teaching |
| Scriptures written in sanskrit are sutra, in Angas | Scriptures written in Pali as Pitakas |
| Salvation by work & Believed in Karmas | Salvation by faith & Believed in karma |
| Strives after his own salvation | Concerned with the salvation of others |